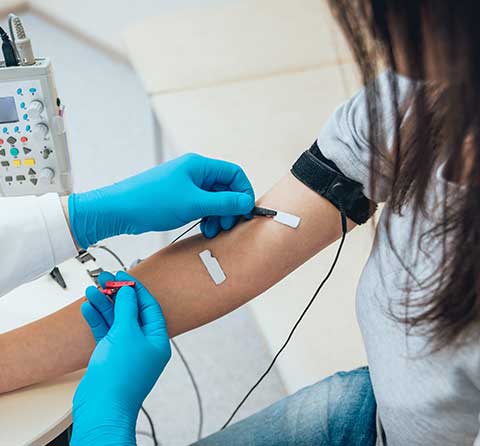
Nerve Evaluations / Electromyography (EMG)
Electrodiagnostic study, commonly known as EMG is a special diagnostic test used to evaluate nerves and muscles.
There are essentially two components of the testing. The first part usually involves the nerve conduction study. Nerve conduction study utilizes electrical stimulation and measures the speed and intensity of electrical signals that travel along a nerve. The second part of the test is the EMG component. EMG stands for electromyography. During this part of the test an electrode is used and it measures electrical activities of the muscles.
The combination of the EMG and the nerve conduction study can determine both peripheral nerve problems as well as muscle problems. EMG and nerve conduction studies are important diagnostic tools to evaluate the neuromuscular system. Nerve injuries from a ruptured disc or carpal tunnel syndrome or from a metabolic reason such as diabetes can be evaluated. Other neuromuscular disorders such as Muscular Dystrophy, Myositis, Lou Gehrig’s disease or Myasthenia Gravis can also be diagnosed with EMG’s and nerve conduction studies.
The electrodiagnostic procedures are usually performed in the office. EMG’s and nerve conduction studies are performed by a specialist with expert training in nerve and muscle disorders. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation specialists or physiatrists who are well trained in the neuromuscular disorders can perform the testing.


